Stopp stemmer
Can low current brain stimulation reduce auditory hallucinations in people with schizophrenia?

Main content
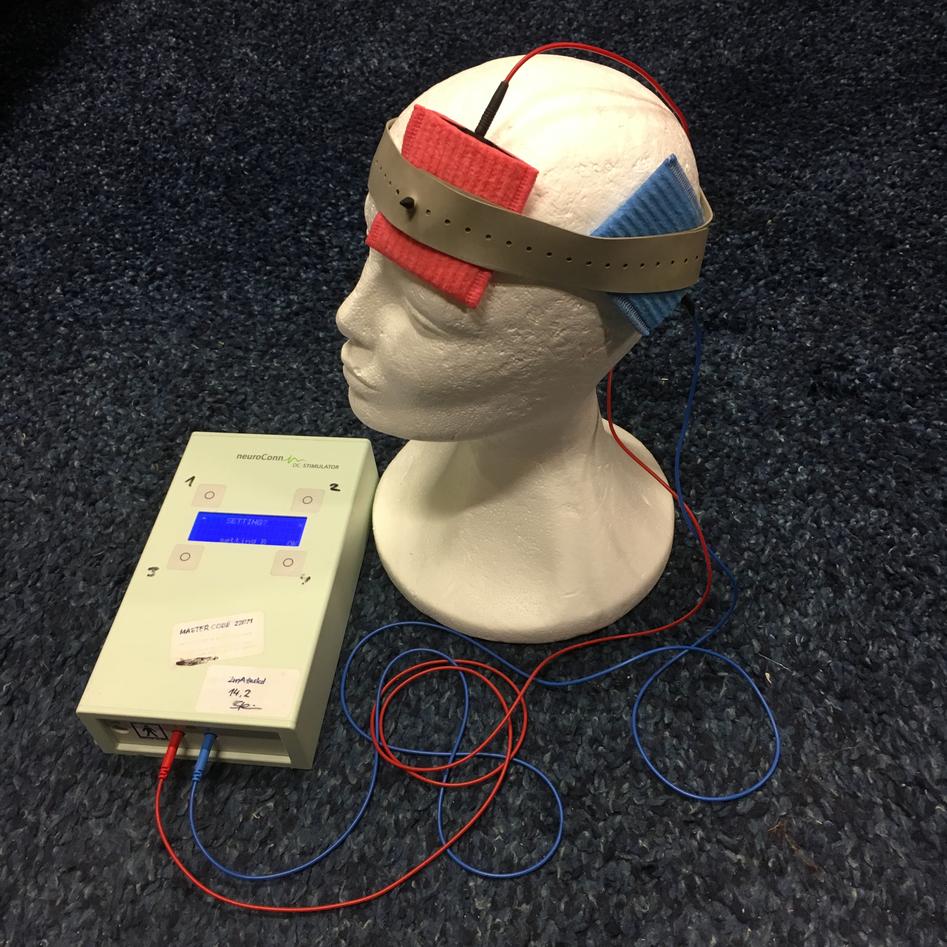
In this project, transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is studied as a possible novel treatment to reduce auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia patients. In tDCS a very low electrical current (2mA) flows between two electrodes that are attached to the head. It is non-invasive and not painful. Most of our participants report a tingling, sometimes itchy sensation only in the beginning and the very end of the stimulation. Patients will be treated with tDCS twice a day with 20 minutes each and a three hour break between the two sessions, for 5 consecutive days.
In order to measure the effect of tDCS on the brain MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) will be done before and after tDCS treatment. The MRI session will last about 1 hour and 15 minutes and includes structural and functional scans of the brain at rest and while performing a verbal task. In addition, we measure Glutamate and GABA, the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain. Both transmitters play a significant role in the neurophysiology of auditory hallucinations.
This is the main project of the FLaSH group financed by the Bergen Research Foundation.
The datacollection for the project is now finished and we are working on the results.